Azure Multi AZ Gateway with DNAT Deployment
This Terraform configuration creates a highly available Azure networking setup with two Enforza gateway servers deployed across different Availability Zones, load-balanced for redundancy and high availability.
This architecture is designed for both outgoing/egress traffic AND incoming traffic with DNAT/port forwarding capabilities for publishing applications from the internet to internal servers.
This configuration deploys a high availability Enforza Gateway solution with both internal load balancing for private subnet routing and an internet-facing load balancer with DNS name for external access.
The Enforza gateways handle all DNAT functionality.
Architecture Overview
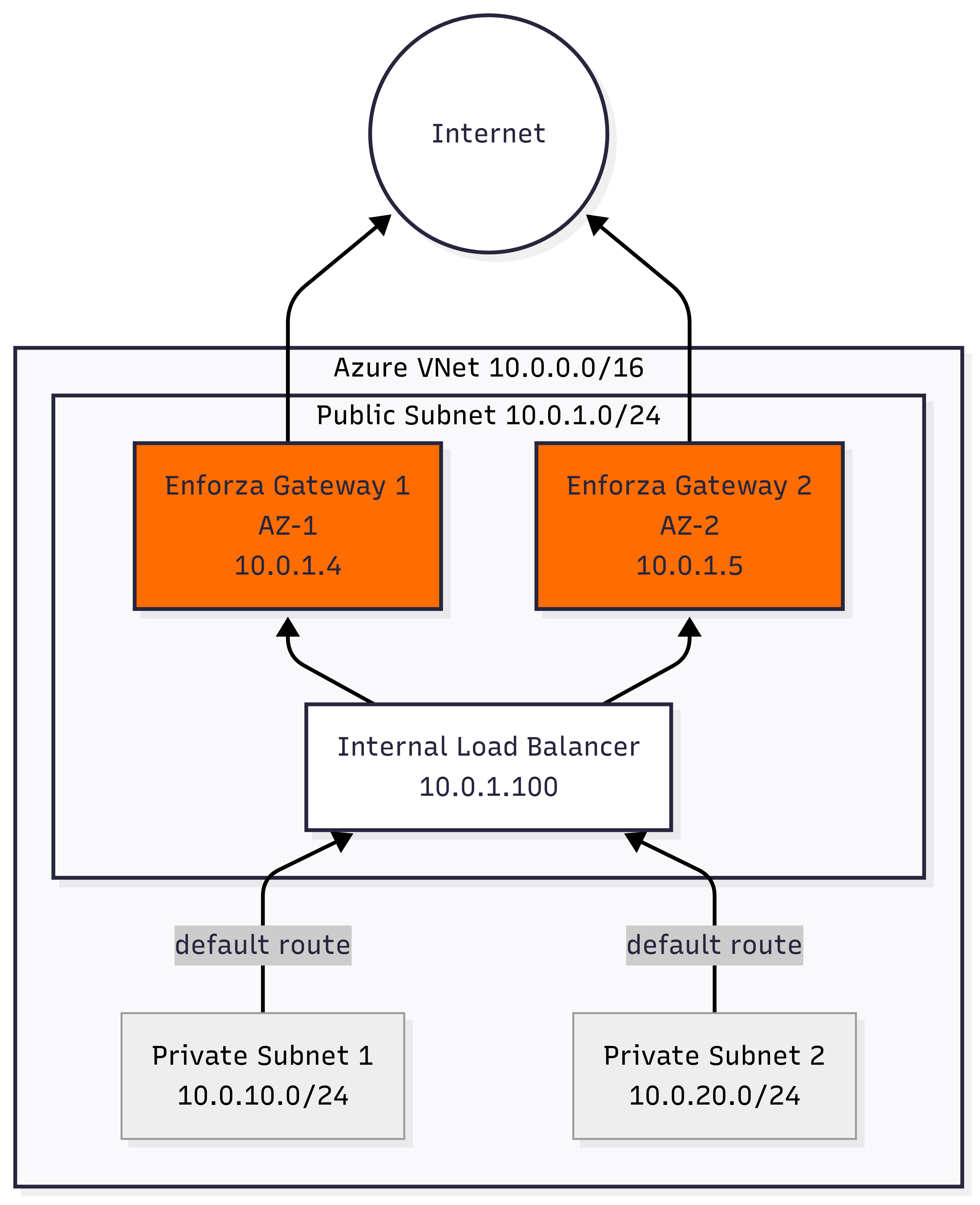
- 2 Enforza Gateways deployed across Azure availability zones 1 & 2
- Internal Load Balancer (10.0.1.100) for private subnet routing
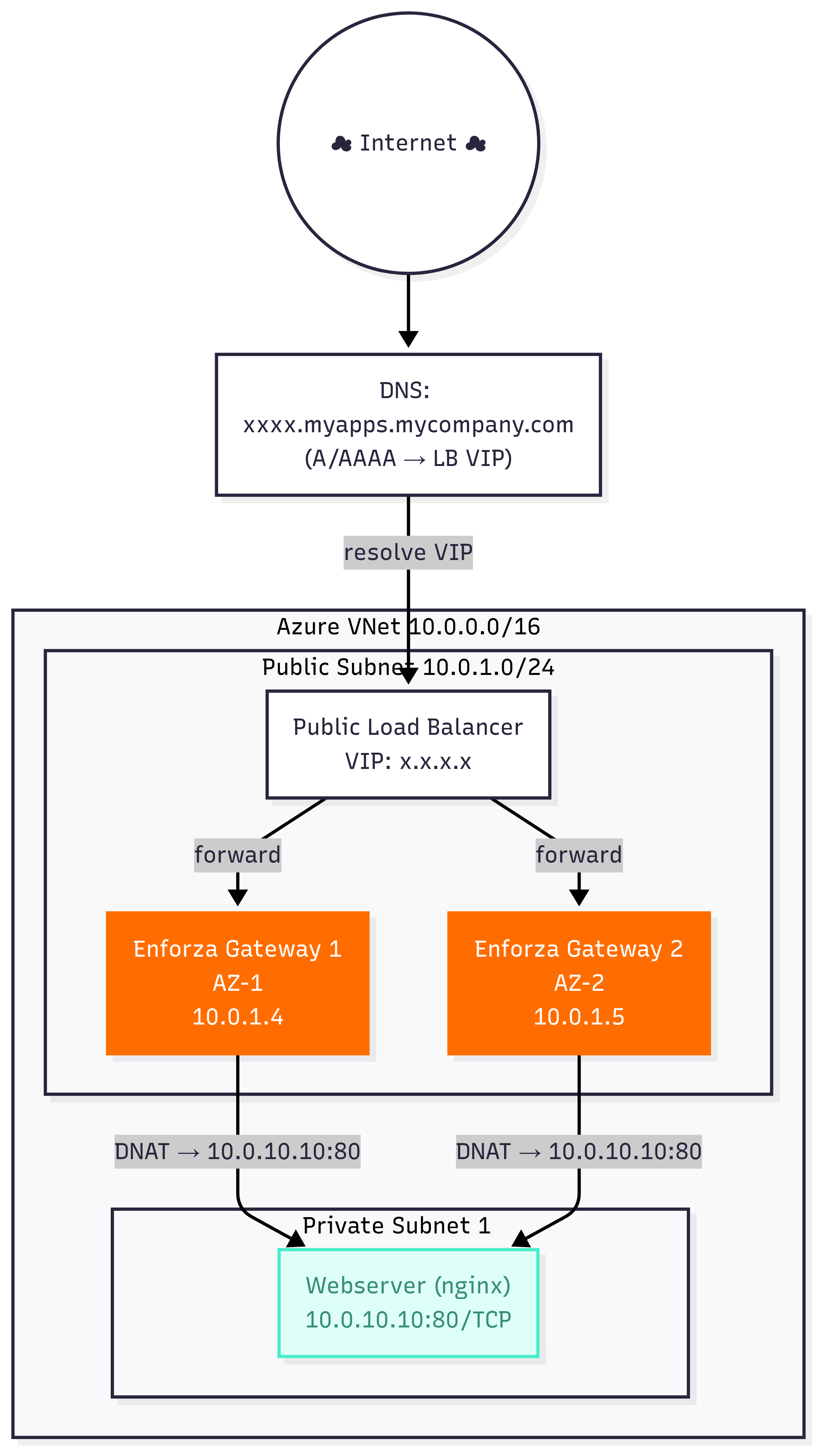
- External Load Balancer with public IP and DNS name for internet access
- Dual load balancer setup: Internal for routing + External for DNAT/DNS
Network Design
Architecture Diagram (Egress)
Architecture Diagram (Ingress/DNAT)
Components Created
Network Infrastructure
- VNet: 10.0.0.0/16 address space
- Public Subnet: 10.0.1.0/24 (contains both Enforza gateways and load balancers)
- Private Subnet 1: 10.0.10.0/24 (routes via internal load balancer)
- Private Subnet 2: 10.0.20.0/24 (routes via internal load balancer)
HA Enforza Gateway Setup
- Gateway 1: enforza-ha-gateway-1 (10.0.1.4) in AZ-1
- Gateway 2: enforza-ha-gateway-2 (10.0.1.5) in AZ-2
- VM Size: Standard_B1s with Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (configured as Enforza Gateway)
- Public IPs: Each gateway has its own public IP for management
- Security: NSG with "permit any any" rules
- Features: Enforza agent automatically installed on both gateways
Load Balancer Configuration
Internal Load Balancer (10.0.1.100)
- Purpose: Routes traffic from private subnets to healthy gateways
- Protocol: All traffic (protocol = "All", port = 0)
- Health Probe: TCP/22 to gateways
External Load Balancer (Public IP + DNS)
- Purpose: Provides internet access with DNS name and forwards all traffic to gateways
- Protocol: All traffic (protocol = "All", port = 0) - same as internal LB
- Health Probe: TCP/22 to gateways
- DNS: Automatic FQDN assignment for easy access
- DNAT: Enforza gateways handle all DNAT functionality
Route Tables
- Private Subnets: Default route (0.0.0.0/0) → Internal Load Balancer (10.0.1.100)
- Load Balancers: Distribute traffic to healthy gateways
- Internet Access: Private subnet VMs route through HA gateway cluster
Quick Start
-
Clone the repository and navigate to the Azure Multi-AZ with DNAT directory:
git clone https://github.com/enforza/azure-terraform.git
cd azure-terraform/ha-multi-az-with-dnat -
Authenticate to Azure:
az login -
Configure variables:
cp terraform.tfvars.example terraform.tfvars
# Edit terraform.tfvars with:
# - Your subscription ID
# - Your Enforza company ID
# - Authentication method (password or SSH key) -
Deploy:
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply -
Manage via the Enforza Cloud Controller:
The device(s) will have automatically registered itself in the portal. Login, and under devices, you should see a newly provisioned device with no name. You can see which is which by looking at the details and seeing which Availability Zone the device is provisioned in.
- Add Firewall rule to allow Azure Load Balancer Health Checks
In the Enforza Cloud Controller, you will need to permit a special rule in the MANAGEMENT RULES that allows the Azure platform to perform Load Balancer Health checks - Azure uses a "special" source IP to perform this (168.63.129.16) - and needs to be permitted or the Azure Load Balancer will show as unhealthy and not forward packets to the Enforza Gateways.
- SRC IP = 168.63.129.16
- DST IP = Firewall/Gateway
- PROT = TCP
- PORT = 22
- LOG = DISABLED
- DESCRIPTION = AZURE LB HEALTHCHECKS

- Enable "FORCE RETURN" in the DNAT RULES
In the Enforza Cloud Controller when you create your DNAT rules, in a HA configuration like this, you need to ensure that the FORCE RETURN option is selected.
This ensures that the destination server returns the traffic to the same Enforza Gateway that performed the incoming DNAT session - this stops asymmetric routing and possible failed sessions.

-
Test HA gateways and external access:
# SSH to gateway 1
ssh azureuser@<gateway_1_public_ip>
# SSH to gateway 2
ssh azureuser@<gateway_2_public_ip>
# Test external DNS name
nslookup enforza-ha-gw-<random>.uksouth.cloudapp.azure.com
Authentication Options
Choose ONE method in terraform.tfvars:
Option 1: Password Authentication
admin_password = "YourSecurePassword123!"
Option 2: SSH Key Authentication (Recommended)
ssh_public_key = "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2E... your-key-here"
Enforza Company ID
enforza_companyId = "d4ff4171-cdaa-40f8-8663-748e22b15c7c"
You can get your enforza_companyId from the Enforza Cloud Controller portal here and navigating to "Profile" and copy/pasting Company ID.
High Availability Features
Automatic Failover
- Load Balancer Health Probes: Continuously monitor gateway health
- Traffic Distribution: Healthy gateways automatically receive traffic
- Zone Redundancy: Gateways in separate AZs for zone-level failure protection
Scaling and Resilience
- Active-Active: Both gateways handle traffic simultaneously
- No Single Point of Failure: Load balancer distributes across healthy nodes
- Zone Isolation: AZ-1 failure doesn't affect AZ-2 gateway
Network Routing
- Private Subnets: Route all traffic via internal LB (10.0.1.100)
- Internet Access: External LB provides public access point with DNS name
- IP Forwarding: Enabled on gateway NICs for proper routing
- Full Transparency: Both load balancers forward all traffic (protocol = "All")
DNAT and External Access
External Access Methods
After deployment, you'll have multiple access options:
-
DNS Name: The external load balancer provides a DNS name like:
enforza-ha-gw-<random>.uksouth.cloudapp.azure.com -
Direct Gateway IPs: Each gateway has its own public IP for management
-
Load Balanced Access: All traffic forwarded to gateways:
- External LB forwards ALL protocols and ports to healthy gateways
- Enforza gateways handle DNAT, port mapping, and traffic processing
- No port restrictions - full transparent forwarding
Security & DNAT
- Enforza DNAT: Gateways handle all DNAT, port mapping, and traffic processing
- NSG: Permissive rules on gateways (Enforza agent handles security)
- Enforza Agent: Automatically installed and configured
- Multiple Auth: Support for password or SSH key authentication
Cost Estimate
Monthly cost: ~$80-100 (UK South region)
- 2x Standard_B1s VMs: ~$30-40/month
- 2x Load Balancers: ~$20/month
- Storage (Premium SSD): ~$10/month
- 2x Public IPs: ~$6/month
- Networking: ~$5-15/month
Still significantly cheaper than Azure Firewall (~$900/month)
Benefits Over Single Gateway
✅ High Availability: No single point of failure
✅ Zone Redundancy: Protection against AZ-level outages
✅ Load Distribution: Better performance under load
✅ Automatic Failover: Seamless traffic redirection
✅ DNAT Capability: External access with port forwarding
✅ DNS Integration: Easy external access with FQDN
✅ Scalable: Easy to add more gateways
✅ Cost Effective: Still ~90% cheaper than Azure Firewall
Troubleshooting
Gateway HA Issues
- Check AZ availability:
az vm list-skus --location uksouth --zone-details - Verify load balancer health: All backend pool members should be healthy
- Test individual gateways: SSH to each gateway and verify Enforza agent
Load Balancer Issues
- Check backend pool:
az network lb address-pool show - Verify health probes: Ensure gateways respond on probe port
- Route table verification: Confirm private subnets route to LB IP
- External LB DNS: Verify DNS resolution works
Private VMs can't reach internet?
- Verify route table association: Private subnets → Internal Load Balancer
- Check gateway health: Both gateways should be healthy in both LBs
- Enforza agent status: Verify agents are running on both gateways
DNAT not working?
- Check external LB: Verify traffic reaches gateways
- Enforza configuration: Ensure DNAT rules are configured in Enforza portal
- NSG rules: Verify traffic is allowed through NSGs
Usage Examples
Deploy Private VMs (Optional)
After creating the gateway, you can deploy VMs in the private subnets:
# Example: Add to main.tf to create private VM
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "private_vm" {
name = "private-vm-nic"
location = azurerm_resource_group.main.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.main.name
ip_configuration {
name = "internal"
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.private_1.id # or private_2
private_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"
}
}
Monitor Traffic
SSH to the gateway and monitor routing:
# Watch traffic flowing through gateway
sudo tcpdump -i any -n host 10.0.10.0/24 or host 10.0.20.0/24
# Check routing table
ip route show
# View iptables NAT rules
sudo iptables -t nat -L
Test External Access
# Test DNS resolution
nslookup enforza-ha-gw-<random>.uksouth.cloudapp.azure.com
# Test external connectivity
telnet enforza-ha-gw-<random>.uksouth.cloudapp.azure.com 80
Customization
Change VM Size
vm_size = "Standard_B2s" # More powerful
vm_size = "Standard_B1ls" # Even cheaper (burstable)
Modify Network Ranges
vnet_address_space = ["192.168.0.0/16"]
public_subnet_prefix = "192.168.1.0/24"
private_subnet_1_prefix = "192.168.10.0/24"
private_subnet_2_prefix = "192.168.20.0/24"
Geographic Region
location = "eastus2" # Change deployment region
Security Note
This configuration uses "permit any any" NSG rules for simplicity. In production:
- Restrict SSH to specific source IPs
- Implement more granular firewall rules
- Consider Azure Bastion for secure access
- Use Key Vault for credentials
- Configure DNAT rules appropriately in Enforza portal
Clean Up
terraform destroy
This will remove all created resources and stop billing.